SeptoPatch
Human Donor Fascia Lata for Septal Perforation Repair
Nasal septal perforation repair is widely recognized in the published literature as a technically demanding procedure with variable outcomes. Reports describe success rates that differ significantly based on perforation size, tissue quality, surgical technique, and graft selection.
SeptoPatch is a human donor fascia lata patch developed to provide surgeons with a standardized biologic graft option intended for use in septal perforation repair.

A Biologic Graft Option for a Complex Surgical Challenge
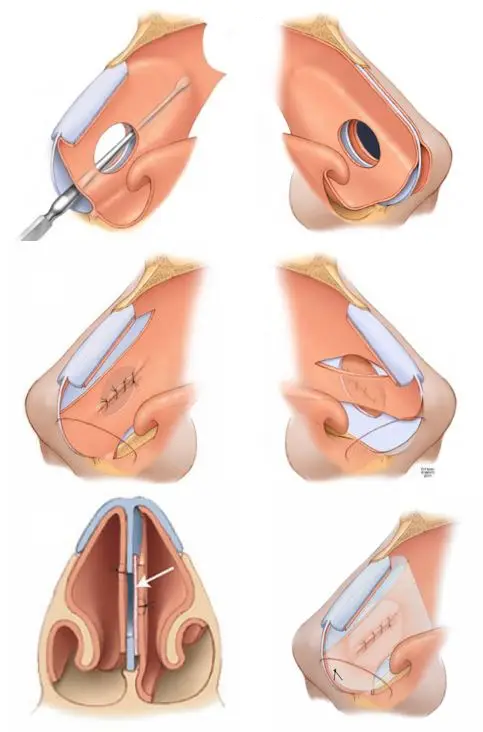
Typical Septal Perforation Repair Technique (Illustrative)
Published surgical techniques commonly describe septal perforation repair using bilateral mucosal flap elevation with placement of an interposition graft between the flaps.
In this approach, mucoperichondrial flaps are carefully elevated on each side of the septum while preserving blood supply. An interposition graft is then positioned between the flaps to span the perforation. The graft serves as a biologic scaffold and structural layer while the mucosal flaps are advanced and closed over it. Internal support, such as nasal splints or temporary stabilization, may be used during the healing phase.
This multilayer configuration is described in the literature for small, moderate, and selected large septal perforations and is intended to reduce tension at the repair site while supporting mucosal healing.
SeptoPatch is designed for use as an interposition graft within this commonly described repair framework.
Why Are Septal Perforation Repairs Challenging?
Published studies describe multiple factors that contribute to the complexity of septal perforation repair, including:
- Limited availability of healthy mucosal tissue
- Reduced vascularity, often related to prior nasal surgery
- High tension at closure sites
- Larger or irregular defects
- Scarred or fragile septal tissue
The literature suggests that these factors may contribute to inconsistent closure rates and have led some surgeons to favor conservative management over surgical repair in selected cases.
Interposition Grafts in Septal Repair
Clinical literature suggests that the use of an interposition graft may be associated with improved closure rates compared to flap-only techniques in septal perforation repair. Interposition grafts are described as providing:
- Structural support across the defect
- A scaffold for mucosal regeneration
- Reduction in tension on advancing flaps
Multiple published studies have evaluated fascia-based grafts as interposition materials in this setting.
Why Fascia Lata?
Human fascia lata has been described in the literature as a commonly used biologic graft in reconstructive procedures. Studies suggest that fascia lata offers a combination of tensile strength, flexibility, and handling characteristics that may be favorable for septal repair applications.
Published reports evaluating donor and autologous fascia lata in septal perforation repair have described closure rates in the range of approximately 80–90 percent in selected patient populations, including larger defects, when used as part of multilayer repair techniques.
These findings reflect reported outcomes in the literature and may vary based on surgical technique, patient factors, and defect characteristics.
SeptoPatch Design Rationale
SeptoPatch standardizes human donor fascia lata into a configuration selected for septal perforation repair.
Product Specifications:
- Material: Human Donor Fascia Lata
- Dimensions: 30 mm x 30 mm
- Thickness: Greater than 0.20 mm, consistent with native donor-derived fascia
- Configuration: Single sterile patch
The dimensions are intended to allow surgeons to trim the graft to match defect geometry while maintaining adequate surface area for coverage.
Potential Clinical Considerations
Based on published literature and reported surgical experience, donor fascia lata grafts have been described as offering:
- Consistent handling characteristics
- Elimination of donor site morbidity associated with autologous harvest
- Structural support without the need for permanent synthetic implants
Use of SeptoPatch does not alter the technical demands of septal perforation repair, which remain dependent on surgeon technique, tissue quality, and patient-specific factors.
Comparison to Commonly Described Alternatives
The literature describes several graft materials used in septal perforation repair, including autologous fascia, cartilage, acellular dermal matrices, and synthetic supports. Studies suggest that each material presents tradeoffs related to handling, availability, and integration.
Fascia lata has been described as offering a balance of strength and flexibility without the additional operative steps required for autologous tissue harvest.
Intended Use
SeptoPatch is intended for use by qualified healthcare professionals as a soft-tissue interposition or reinforcement graft in nasal septal perforation repair.
Important Note
The clinical outcomes associated with septal perforation repair vary widely and depend on multiple factors. The information presented reflects findings reported in the published literature and is provided for educational purposes only. Individual patient outcomes may vary.
Check Out Our Resource Center for All Certifications, FDA Regulations and Clinical Evidence
Download the BioMed app to share documents on-the-go!
Ordering Information
Code | Description | Size | Thickness |
BE4030FD | SeptoPatch – Freeze Dried | 30 MM x 30 MM | Greater Than 0.2 MM |